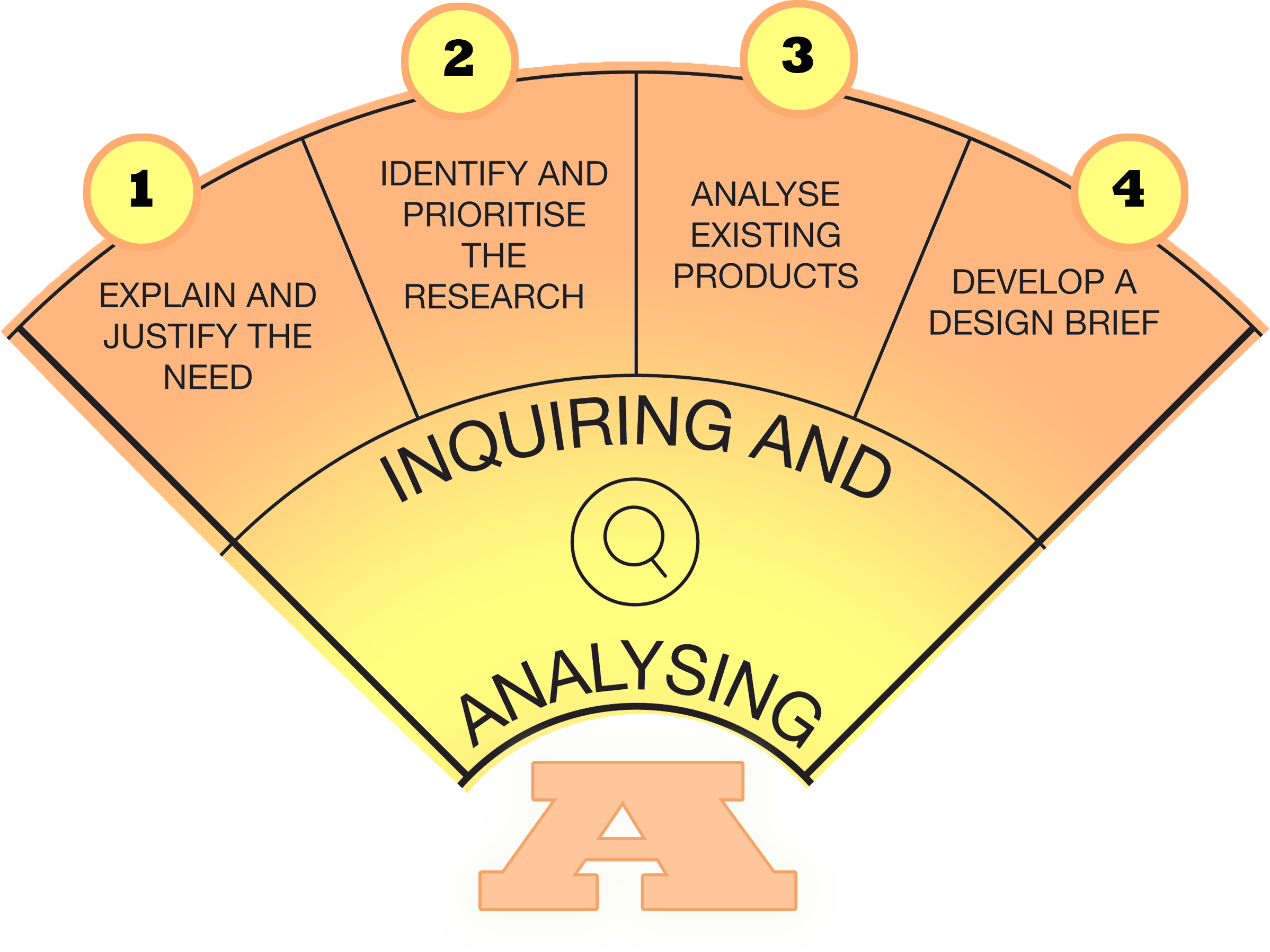
The Design Challenge
As a civil engineer working with a team at Stockholm International School, your job is to help design a new bridge. This bridge is needed to replace the Norra Järnvägs bridge in the city of Stockholm. The new bridge solution must meet important requirements, like having a span of 270-280 meters with no pillars in the middle, being efficient to build, and only carrying rail freight (trains that move goods). The bridge also can’t be taller than 100 meters. Your design needs to be strong and safe enough to handle the weight of the trains and make sure everything runs smoothly.

SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a way to take what we have learned about a product’s Strengths and Weaknesses and predict the advantages (Opportunities) and disadvantages (Threats) of the product in a certain context.
Watch the video below about SWOT analysis.
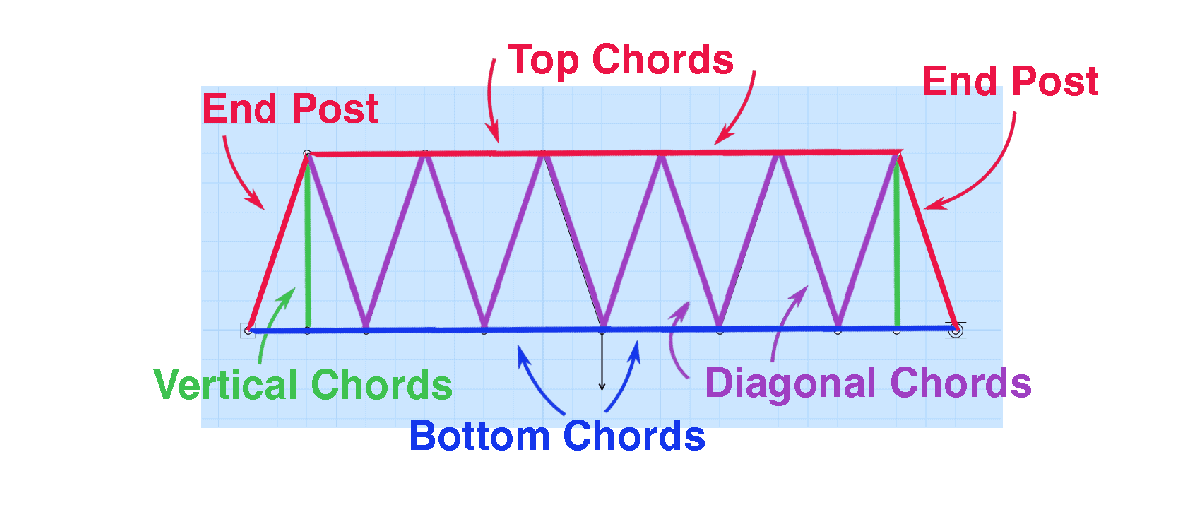
Truss Forces & Terminology
The diagram below shows top, bottom, diagonal, and vertical chords. We also see end posts.
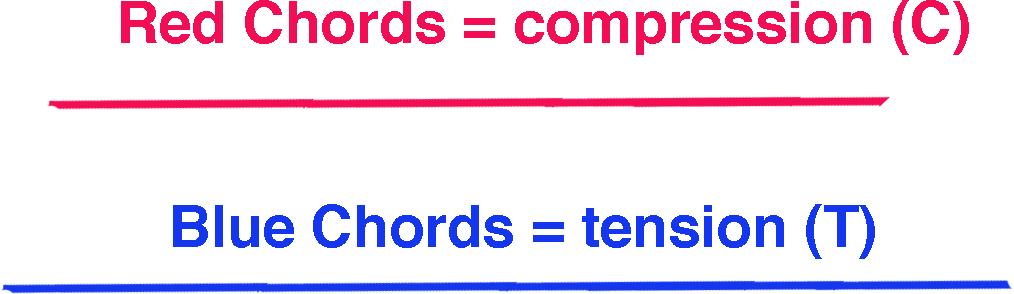
Green Chords = Zero Force (0)
Purple Chords = either C or T, depending on the truss type
Evaluating efficiency

-
- Load Distribution:
- Adding more members can help spread forces evenly.
- While extra members can aid load distribution, too many may not improve the design and can increase weight and cost, reducing efficiency.
- Zero-force members do not contribute to load support.
- Forces near the load point should be evenly distributed to prevent failure.
- Load Distribution:
-
- Length of Members:
- Shorter members in compression are generally more efficient.
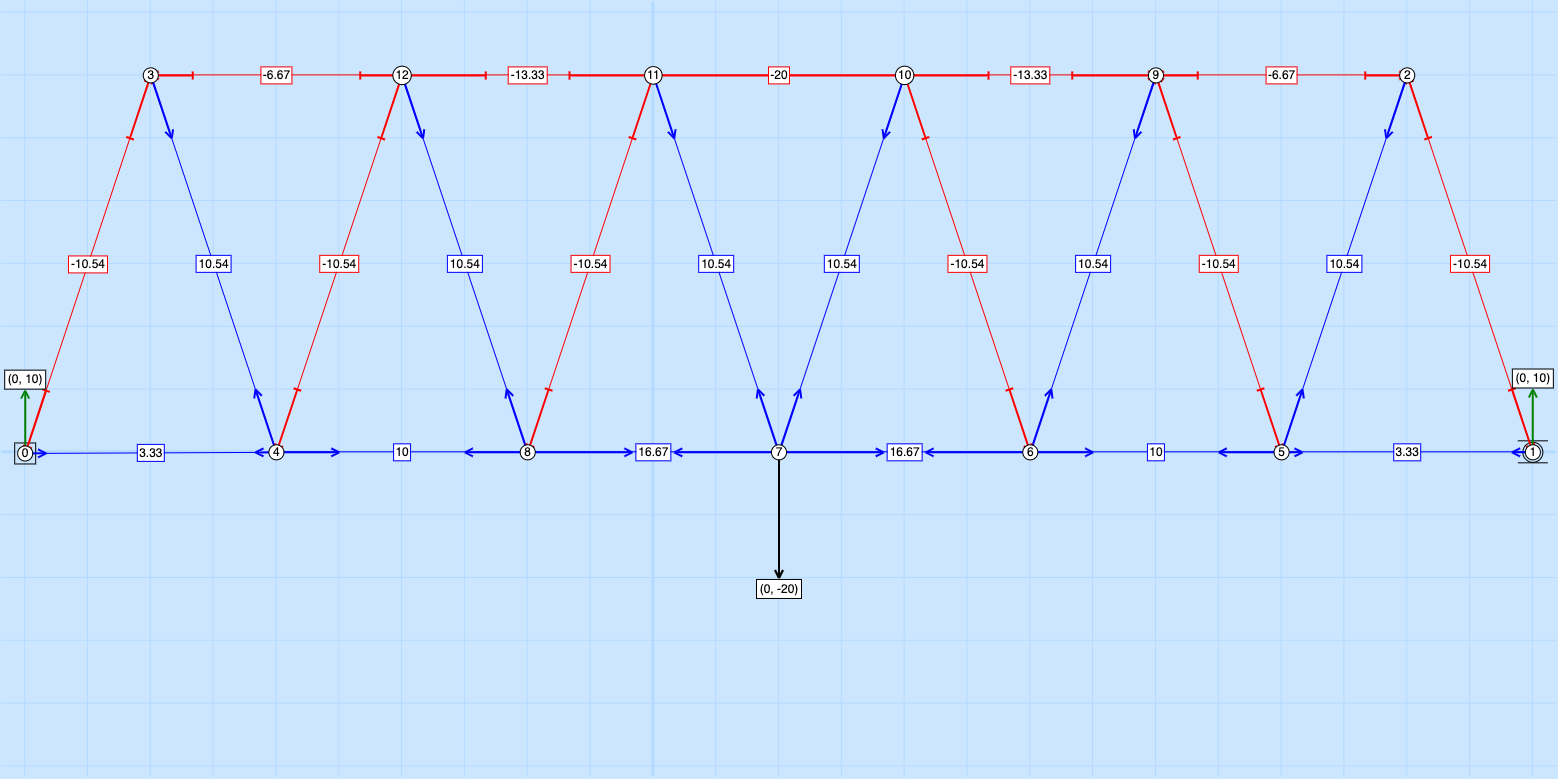
Force Diagrams
Below are diagrams of various truss design types. All of the bridges have a center load point which is shown by the downward pointing arrow.
When looking at the Warren Truss:
The chord with -10.54 is in more compression than the chord with -6.67
The chord with 16.67 is in more tension than the chord with 10.
The members labeled with “0” are zero force members. This means that they aren’t in compression or tension and are redundant.
Answer the following questions*:
Question 1) What are the similarities and differences between a Howe and a Pratt Truss?
-
Compare the forces on the top and bottom chords, and vertical chord near the load point when answering this question.
Question 2) Which of these two designs do you think is most efficient? Use the information from the force diagrams to support your answer.
Question 3) When comparing the Howe Truss to the K truss, which design do you think is most efficient? Give two examples of why you think this way.
*Use the terminology above when writing about the designs.
Warren Truss
Warren Truss with Verticals
Notice how this bridge has extra members that don’t support weight, called zero-force members. These extra parts add unnecessary weight, making the bridge less efficient.

Howe Truss
Look at how the forces of C and T differ on the Howe and Pratt. What are the main differences?
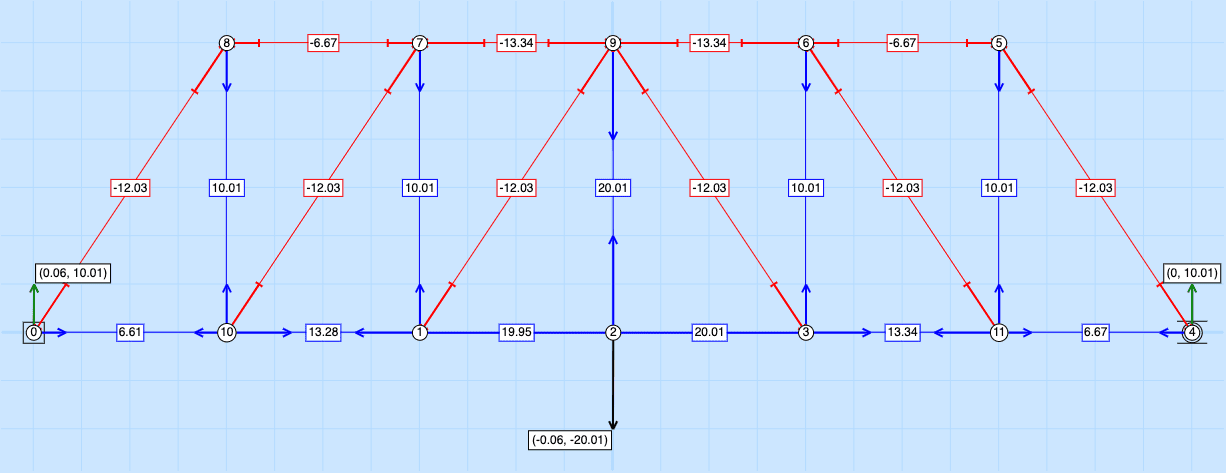
Pratt Truss
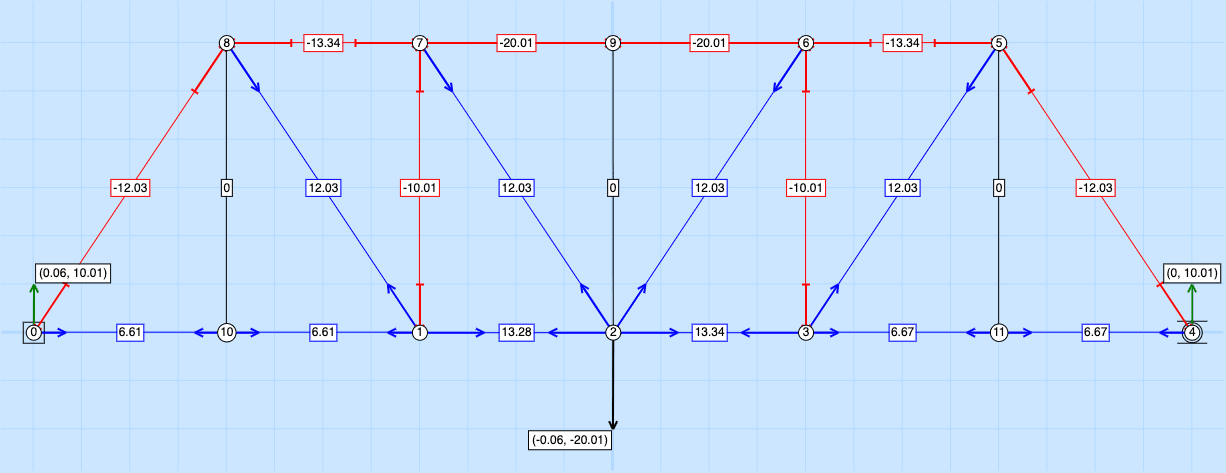
K Truss
The design uses more members than a Howe or Pratt. How does that effect efficiency?


